|
A 6-month-old male infant 3rd in the sibling order,
born at term to nonconsanguineous parents was noticed to have bilateral
proptosis and deformity of the thumbs and toes at the time of birth. The
baby was admitted with the presenting complaints of large size of the
head and inability to attain expected milestones. Examination revealed a
child with a large head, head circumference of 49.5 cm (>95th
percentile) with scaphocephaly and fused sagital suture with a palpable
ridge in the posterior 2/3rd. Anterior fontanel was wide open, there was
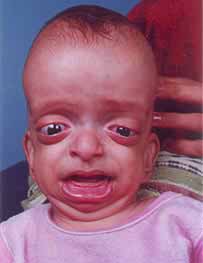
prominence of the frontal bone with high low set ear (Fig.
1). Orbits were small with
proptosed eyeballs and exposure keratitis. Other positive features were
hypoplastic maxillae, depressed bridge of the nose, hypertelorism and
pectus excavatum. Adduction and flexion deformities were present in toes
and thumbs. There was no significant organomegaly. The child could not
sit, nor could turn over from prone to supine position. There was no
visual following and ocular fundi showed atrophic changes. CT Scan
revealed bilateral, lateral and third ventricular dilatation, proptosis
and dolicocephalic skull. The fourth ventricle was normal.
Crouzon’s syndrome is one of the commonest
syndromes associated with craniosynostosis. It was first described in
1912 by Crouzon in a mother and daughter. Cardinal features of the
syndrome are craniosynostosis, small orbits, proptosis and maxillary
hypoplasia. Occa-sionally, it is associated with hydrocephalus as in
this case. It is autosomal dominant in inheritance with variable
expression. Mutation in the fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 gene
(FGFR2) which maps to chromosome 10q25-q26 causes Crouzon syndrome.
A.K. Dubey,
R.K. Gupta,
Department of Pediatrics,
Base Hospital,
Delhi Cantt 110 010,
India.
|
|
|
Fig. 1. Photograph showing large head,
proptosed eyeballs, frontal bone prominence, depressed bridge of nose,
hypertelorism, hypoplastic maxillae and big low set ears.
|
|
