|
Rajbinder Kaur
Dehiya
Deepa Bhartiya
Chhaya Kapadia
Meena P. Desai
From
the Cell Biology Department, Research Society, B.J. Wadia Hospital
for Children and Institute of Child Health, Acharya Donde Marg,
Parel, Mumbai 400 012, India
Reprint requests:
Dr. Deepa Bhartiya,Cell Biology Department, B.J. Wadia Hospital
for Children, Acharya Donde Marg, Parel, Mumbai 400 012, India
Manuscript
received: June 17, 1999;
Initial review completed: August 10, 1999;
Revision accepted: March 21, 2000
The
actions of growth hormone (GH), a major regulator of growth, are
mediated via Insulin like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1), produced by the
liver(1). Almost 95% of IGF-1 in circulation is present in a 150 kDa
complex, with its binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) and another protein,
Acid Labile Subunit (ALS,2). This complex stabilizes IGF-1, prolongs
its half-life and also regulates its bio-availability to growing
tissues(2). These peptides viz., IGF-1, IGFBP-3 and ALS
appear to be more stable than GH (which is pulsatile in nature), show
minimum diurnal variation and are being used to screen for GH
deficiency(3) in an easier manner than the conventional GH
measurement. They are also being studied in cases of GH
insensitivity(4), intrauterine growth retardation(5), polycystic
ovarian syndrome(6) and central precocious puberty(7).
It is a well
established fact that children of developing countries do not attain
same level of growth as their Western counterparts. Compari-sons with
the European countries show that even affluent Indians are shorter and
lighter(8,9). It has been shown in the past, that using Western
percentiles, there would be unnecessary investigation for short
stature in a third of our normal population(10). Recently, Khadagwat et
al.(11) found that Agarwal charts(8,9) were better representative
of growth of normal Indian children than the NCHS or ICMR charts (the
latter were based on Indian children of low socio-economic status
families and the study was conducted four decades ago).
Since IGF-1, IGFBP-3
and ALS are essentially involved in postnatal growth, we have analyzed
their levels in healthy children and adolescents (from birth to 20
years of age) residing in Mumbai suburbs and have also made
comparisons between present study data and that available for Western
population.
The study population
included 434 children/adolescents (new-born to 20 years of age;
atleast 10 males and 10 females per year of age). Samples from healthy
full-term new borns, delivered normally after uncomplicated
preg-nancies and weighing more than 2.5 kg at birth, were collected
from a maternity hospital. To collect samples from older
children/adolescents, camps were organized in large residential
complexes in Mumbai suburbs. The children included, belonged to
well-to-do higher to middle class families with monthly income over Rs.
5000. We worked on the premise that our study population had maximum
growth potential, since they did not belong to low socio-economic
status families. Nutrition was not a limiting factor in our population
was further confirmed by plotting the heights and weights of our study
group on Agarwal's growth charts(8,9) generated on children belonging
to affluent class of our community. Almost 90% of our children had
their heights and weights falling within the 3rd and 97th percentile
of Agarwal charts. As weight for height is the best anthropometric
index of nutrition, using EPIINFO software, we found 96% of our
children above 10 years of age to be more than 90% of mean weight for
height by NCHS standards. However, in age group below 10 years, 50% of
present study children were more than 50% of mean weight for height by
NCHS standards. The children had no history of systemic illness and
also no obvious problem in growth/height. None of the girls included
in the study had delayed onset of menses. Two ml of blood was
collected and the serum was stored in aliquots at –70°C till
further analysis.
Measurement of IGF-1,
IGFBP-3 and ALS: Commercial
kits from Diagnostic Systems Laboratories, USA were used to measure
all the three peptides.
Statistical Analysis:
Body Mass Index (BMI) was calculated using the formula Weight
(kg)/Height2 (meters). Data was analyzed using the Statistical
Analysis Software (SAS, North Carolina, USA). Correlation between the
peptides and various clinical parameters such as age, weight, height
and BMI were studied by multivariate analysis. Graphs were made using
the Microsoft Excel Software. Statistical significance of difference
between the present study and the Western population(12) was
determined by the Students "t" test (two-tailed). A ‘p’
value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Levels of all the three
peptides, from birth to 20 years of age, are shown in Tables I-III.
A steady increase in the circulatory levels of all the three peptides
with age was observed. IGF-1 levels in circulation, showed more
dramatic alterations in both the sexes, compared to IGFBP-3 and ALS.
Almost a thirty fold increase in IGF-1 and a five fold increase in
IGFBP-3 levels was noticed at 12-14 years in girls and 15 years in
boys followed by a decline. Circulatory levels of ALS showed a seven
and a nine fold rise at 14 years in girls and 17 years in boys,
respectively, followed by a decline thereafter.
Multivariate analysis
with age and BMI as the independent variables revealed that all the
three peptides correlated significantly with BMI in females and with
age in males.
On comparison of IGF-1
and IGFBP-3 levels (mean ±SE) obtained in present study with the
Western population , IGF-1 levels were observed to be lower in the
present study population (Fig. 1) than their Western
counterparts, at all ages in both the sexes, IGFBP-3 levels showed
considerable overlap between the two popula-tions except at birth,
where IGFBP-3 levels were significantly lower in the present study
group.
In the present study,
circulatory levels of IGF-1, IGFBP-3 and ALS were studied in Indian
children residing in Mumbai suburbs. Unlike IGFBP-3 and ALS, IGF-1
showed more dramatic changes with age. Though levels increased
gradually till 10 years of age, a thirty-fold rise was observed during
adolescent years. Early peaks were observed in girls (12-14 years) as
compared to boys (15 years) in accordance with the earlier sexual
maturation in girsl(13). Interestingly ALS levels peaked later in both
girls (14 years) and boys (17 years).
In agreement with
earlier studies conducted in healthy Japanese(1). Caucasians(13), and
Spanish(14) children, the present data revealed distinct age related
alterations in the circulatory levels of all the three peptides.
However, peak values of IGF-1 were attained at different ages in all
the three groups.
Environment and
genetics are the major factors that regulate the physical growth of an
individual. Vijayaraghavan et al.(15) had earlier reported that
well-to-do Indian girls, without any apparent dietary and
environmental constraints were as tall and heavy as American girls up
to 12 years of age and considerable deviations were noted in
adolescent period. The differences in the growth curves of Indian and
American girls emerged and widened to result in a difference of 5 cm
at the 18th year, a difference which occurred almost entirely between
the 12th and 18th year of age. Although, the number of observations
per year are less in the present study, it is of interest to note that
IGF-1 levels were lower at all ages, as compared to the Western norms,
and achieved statistical signi-ficance in the post-pubertal period (Fig.
1).
Extensive studies need
to be carried out to evaluate the clinical usefulness of these
peptides in Indian children having various endocrine defects.
Table
I__Levels of IGF-1,
IGFBP-3 and ALS in Children (New-born to Five Years)
Age
(Yr) |
n |
Mean |
SD |
Range |
Percentiles |
| |
5th |
10th |
25th |
50th |
75th |
90th |
95th |
| IGF-1 |
| 0 |
20 |
14.1 |
4.7 |
9.6-26 |
9.8 |
10.5 |
12 |
12.8 |
13.5 |
20.5 |
26 |
| 1 |
20 |
23.1 |
16.7 |
10.5-66 |
10.5 |
10.5 |
14 |
19 |
20 |
66 |
66 |
| 2 |
20 |
43.8 |
27.9 |
9-120 |
9 |
20 |
23.5 |
39.5 |
47.5 |
79 |
120 |
| 3 |
20 |
48.1 |
29.5 |
10-120 |
16 |
17 |
23 |
33.5 |
68 |
90 |
120 |
| 4 |
20 |
49.3 |
24.1 |
12.5-105 |
12.5 |
16 |
34 |
47.5 |
58 |
92 |
105 |
| 5 |
22 |
67.7 |
57.8 |
16.5-260 |
27 |
29 |
30 |
52.5 |
72 |
145 |
180 |
| IGFBP-3 |
| 0 |
20 |
1090.3 |
342.1 |
520-1950 |
562.5 |
642.5 |
930 |
1025 |
1275 |
1550 |
1825 |
| 1 |
20 |
1496.7 |
482.5 |
830-2150 |
830 |
830 |
1000 |
1500 |
1850 |
2100 |
2100 |
| 2 |
20 |
2478.1 |
705.9 |
1550-4000 |
1550 |
1650 |
1925 |
2400 |
2975 |
3500 |
4000 |
| 3 |
20 |
2200 |
991.3 |
670-4500 |
800 |
940 |
1650 |
2000 |
2700 |
3700 |
4500 |
| 4 |
20 |
2522.2 |
927.4 |
1050-4500 |
1050 |
1350 |
1850 |
2300 |
3300 |
3550 |
4500 |
| 5 |
22 |
2525.5 |
963.7 |
1010-4800 |
1450 |
1450 |
1600 |
2450 |
3100 |
3550 |
4000 |
| ALS |
| 0 |
20 |
4.1 |
2.2 |
1.1-11 |
1.3 |
1.8 |
2.8 |
3.9 |
4.7 |
7.1 |
9.1 |
| 1 |
20 |
7.9 |
4.8 |
1.7-16.5 |
1.7 |
1.7 |
4.5 |
6.4 |
11 |
16.5 |
16.5 |
| 2 |
20 |
11.1 |
6.4 |
1.8-30 |
1.8 |
5.5 |
7.3 |
9.9 |
12.8 |
17 |
30 |
| 3 |
20 |
11.5 |
5.3 |
3.9-21.5 |
3.9 |
5.6 |
6.3 |
11.5 |
13.5 |
21.5 |
21.5 |
| 4 |
20 |
14.2 |
5.8 |
7.4-27 |
7.4 |
7.8 |
9.2 |
12.5 |
19 |
22.5 |
27 |
| 5 |
22 |
13.7 |
5.8 |
4.4-25 |
6.6 |
8 |
10 |
11.5 |
17.5 |
23 |
24 |
Table
II__Levels of IGF-1,
IGFBP-3 and ALS in Girls (Six to Twenty Years).
|
Age
(Yr) |
n |
Mean |
SD |
Range |
Percentiles |
| |
5th |
10th |
25th |
50th |
75th |
90th |
95th |
|
IGF-1 |
| 6 |
10 |
91.4 |
54.7 |
31-190 |
31 |
31 |
48 |
80 |
135 |
190 |
190 |
| 7 |
10 |
96.2 |
45.4 |
38-190 |
38 |
38 |
77 |
90 |
105 |
190 |
190 |
| 8 |
10 |
113.2 |
53.4 |
28-195 |
28 |
42 |
79 |
105 |
147.5 |
190 |
195 |
| 9 |
10 |
217.6 |
189.1 |
51-650 |
51 |
51 |
105 |
145 |
280 |
650 |
650 |
| 10 |
11 |
139.4 |
65.8 |
39-290 |
73 |
86 |
89.5 |
105 |
162.5 |
210 |
290 |
| 11 |
10 |
262.2 |
151.3 |
58-465 |
58 |
58 |
147.5 |
250 |
380 |
465 |
465 |
| 12 |
11 |
393.6 |
182.3 |
92-640 |
135 |
145 |
205 |
470 |
520 |
620 |
640 |
| 13 |
11 |
401.4 |
135.6 |
100-650 |
145 |
280 |
285 |
420 |
490 |
500 |
650 |
| 14 |
10 |
413 |
147.8 |
155-670 |
155 |
202.5 |
350 |
422.5 |
490 |
615 |
670 |
| 15 |
10 |
309.5 |
93.1 |
86-445 |
120 |
190 |
265 |
300 |
365 |
427.5 |
445 |
| 16 |
10 |
302 |
70.6 |
135-390 |
200 |
220 |
240 |
300 |
380 |
385 |
390 |
| 17 |
10 |
221.8 |
55.7 |
115-300 |
122.5 |
122.5 |
195 |
230 |
250 |
300 |
300 |
| 18 |
10 |
306.5 |
107.9 |
170-490 |
170 |
187.5 |
205 |
297.5 |
400 |
465 |
490 |
| 19 |
11 |
244 |
119.4 |
99-510 |
99 |
105 |
145 |
255 |
310 |
320 |
510 |
| 20 |
10 |
262.5 |
114.0 |
150-605 |
150 |
152.5 |
160 |
205 |
360 |
415 |
470 |
|
IGFBP-3 |
| 6 |
10 |
3464.3 |
1263.8 |
1950-4500 |
1950 |
1950 |
2300 |
3100 |
4500 |
5400 |
5400 |
| 7 |
10 |
3100 |
617.0 |
1450-2900 |
2100 |
2100 |
2550 |
3400 |
3650 |
3700 |
3700 |
| 8 |
10 |
3245 |
755.9 |
1800-4100 |
1800 |
2100 |
2850 |
3400 |
3900 |
4100 |
4100 |
| 9 |
10 |
3700 |
1883.7 |
1650-7000 |
1650 |
1650 |
2550 |
2600 |
4400 |
7000 |
7000 |
| 10 |
11 |
3618.2 |
1050.3 |
1800-4800 |
1800 |
2200 |
2900 |
3600 |
4650 |
4650 |
4800 |
| 11 |
10 |
4027.8 |
1243.3 |
1900-6700 |
1900 |
1900 |
3800 |
4000 |
4100 |
6700 |
6700 |
| 12 |
11 |
5331.8 |
1917.6 |
2600-9000 |
2600 |
3200 |
3900 |
5000 |
6900 |
7200 |
9000 |
| 13 |
11 |
4572.7 |
1466.4 |
2900-7000 |
2900 |
3200 |
3300 |
4000 |
5900 |
6700 |
7000 |
| 14 |
10 |
4565 |
949.3 |
3500-6400 |
3500 |
3500 |
3600 |
4725 |
5100 |
5900 |
6400 |
| 15 |
10 |
4305 |
938.8 |
3050-6400 |
3050 |
3275 |
3800 |
4150 |
4500 |
5800 |
6400 |
| 16 |
10 |
4150 |
548.2 |
3050-5100 |
3400 |
3525 |
3800 |
4075 |
4500 |
5025 |
5100 |
| 17 |
10 |
4600 |
1209.3 |
3500-7000 |
3500 |
3500 |
3500 |
4500 |
4950 |
7000 |
7000 |
| 18 |
10 |
4485 |
1078.3 |
2650-6600 |
2650 |
3025 |
3700 |
4550 |
4950 |
5850 |
6600 |
| 19 |
11 |
3663.6 |
1142.0 |
1850-5000 |
1850 |
2000 |
2900 |
3500 |
4650 |
4900 |
5000 |
| 20 |
10 |
3650 |
992.2 |
2500-5800 |
2550 |
2575 |
2700 |
3600 |
4500 |
5100 |
5400 |
|
ALS |
| 6 |
10 |
19.4 |
6.2 |
11.0-28 |
11 |
11 |
14.5 |
18 |
25.5 |
28 |
28 |
| 7 |
10 |
18.7 |
6.4 |
9.4-27 |
9.4 |
9.4 |
15.5 |
20.5 |
23 |
27 |
27 |
| 8 |
10 |
17.7 |
5.6 |
7-27.5 |
7 |
10 |
14.5 |
18 |
20 |
25.3 |
27.5 |
| 9 |
10 |
22.4 |
7.1 |
12-31.5 |
12 |
12 |
18.5 |
24 |
27 |
31.5 |
31.5 |
| 10 |
11 |
21.5 |
7.8 |
10.5-32 |
10.5 |
12 |
14.5 |
21 |
31 |
32 |
32 |
| 11 |
10 |
28.4 |
9.9 |
8.4-37 |
8.4 |
8.4 |
22 |
34 |
35 |
37 |
37 |
| 12 |
11 |
27.6 |
6.5 |
16.5-41 |
16.5 |
22 |
24 |
26 |
32 |
34 |
41 |
| 13 |
11 |
28.9 |
9.0 |
16.5-47 |
16.5 |
19.5 |
23 |
27.5 |
31 |
42 |
47 |
| 14 |
10 |
34.0 |
6.8 |
23.5-44.5 |
23.5 |
26 |
31 |
31.5 |
41 |
43.8 |
44.5 |
| 15 |
10 |
32.5 |
5.9 |
26.5-47 |
26.5 |
27.3 |
29 |
30 |
34 |
41 |
47 |
| 16 |
10 |
31.8 |
7.9 |
21-44.5 |
21 |
21 |
27 |
33 |
37 |
40.8 |
44.5 |
| 17 |
10 |
23.4 |
3.6 |
17.5-29 |
17.5 |
17.5 |
21 |
24 |
25 |
29 |
29 |
| 18 |
10 |
27.4 |
7 |
15-40 |
15 |
18.8 |
23 |
28 |
30 |
37 |
40 |
| 19 |
11 |
25.1 |
5.6 |
13-30 |
13 |
20.5 |
20.5 |
27.5 |
30 |
30 |
30 |
| 20 |
10 |
24.1 |
8.1 |
10.5-36 |
10.5 |
14 |
19 |
22.8 |
32 |
35.5 |
36 |
Table
III__Levels of IGF-1,
IGFBP-3 and ALS in Boys (Six to Twenty Years)
| Age |
n |
Mean |
SD |
Range |
Percentiles |
| (Yr) |
|
5th |
10th |
25th |
50th |
75th |
90th |
95th |
| IGF-1 |
| 6 |
10 |
104.7 |
61.7 |
14-230 |
41 |
42 |
55 |
88 |
130 |
207 |
230 |
| 7 |
10 |
64.1 |
20.8 |
39-98 |
39 |
39 |
47 |
68 |
79 |
98 |
98 |
| 8 |
11 |
81.8 |
39.5 |
26-140 |
26 |
36 |
40 |
84 |
117.5 |
130 |
140 |
| 9 |
10 |
134.2 |
56.7 |
43-210 |
43 |
43 |
100 |
137.5 |
165 |
210 |
210 |
| 10 |
10 |
108.4 |
38.4 |
40-155 |
40 |
45 |
92 |
122.5 |
130 |
151.3 |
155 |
| 11 |
12 |
163.8 |
100.6 |
43-320 |
43 |
51 |
91 |
117.5 |
262.5 |
310 |
320 |
| 12 |
13 |
184.4 |
108.2 |
54-350 |
54 |
85 |
90 |
140 |
310 |
330 |
350 |
| 13 |
10 |
154.3 |
82.4 |
56-310 |
65 |
67.5 |
100 |
118.8 |
215 |
277.5 |
310 |
| 14 |
11 |
265.6 |
164.6 |
38-560 |
68 |
86 |
107.5 |
250 |
370 |
475 |
560 |
| 15 |
11 |
370 |
98.7 |
230-580 |
230 |
260 |
275 |
380 |
415 |
460 |
580 |
| 16 |
10 |
360 |
84.6 |
160-480 |
160 |
235 |
360 |
362.5 |
410 |
455 |
480 |
| 17 |
10 |
299.3 |
165.5 |
100-580 |
102.5 |
108.8 |
140 |
270 |
450 |
535 |
580 |
| 18 |
10 |
316 |
132.8 |
140-640 |
140 |
170 |
240 |
310 |
350 |
500 |
640 |
| 19 |
10 |
286.5 |
92.1 |
190-415 |
180 |
185 |
220 |
242.5 |
390 |
402.5 |
415 |
| 20 |
10 |
265.7 |
106.6 |
65-410 |
65 |
65 |
240 |
255 |
330 |
410 |
410 |
| IGFBP-3 |
| 6 |
10 |
3175 |
713.5 |
1850-4000 |
1850 |
2200 |
2550 |
3150 |
3900 |
3950 |
4000 |
| 7 |
10 |
2014.3 |
480.2 |
1450-3700 |
1450 |
1450 |
1650 |
2100 |
2200 |
2900 |
2900 |
| 8 |
11 |
3286.4 |
1189.8 |
1850-5300 |
1850 |
1850 |
1900 |
3400 |
4200 |
4900 |
5300 |
| 9 |
10 |
3644.4 |
1224.9 |
2000-6200 |
2000 |
2000 |
2800 |
3500 |
4000 |
6200 |
6200 |
| 10 |
10 |
3495 |
950.6 |
2400-5900 |
2400 |
2600 |
3100 |
3300 |
3800 |
4900 |
5900 |
| 11 |
12 |
4004.2 |
1368.6 |
2200-6600 |
2200 |
2250 |
3050 |
3650 |
5200 |
5400 |
6600 |
| 12 |
13 |
3996.2 |
767.7 |
2650-5300 |
2650 |
3200 |
3500 |
3900 |
4600 |
5000 |
5300 |
| 13 |
10 |
4185 |
996.7 |
2450-5900 |
2450 |
2825 |
3800 |
4100 |
4900 |
5600 |
5900 |
| 14 |
11 |
4372.7 |
1528.0 |
2100-7600 |
2100 |
2750 |
3650 |
4200 |
4700 |
6300 |
7600 |
| 15 |
11 |
4768.2 |
1432.2 |
2900-7000 |
2900 |
3400 |
3650 |
4300 |
6600 |
6600 |
7000 |
| 16 |
10 |
4433.3 |
1023.8 |
2900-6200 |
2900 |
2900 |
3850 |
4350 |
4900 |
6200 |
6200 |
| 17 |
10 |
3815 |
884.1 |
2100-5400 |
2100 |
2575 |
3200 |
3925 |
4200 |
4875 |
5400 |
| 18 |
10 |
4145 |
1199.0 |
1250-5400 |
1250 |
2250 |
3900 |
4350 |
4950 |
5250 |
5400 |
| 19 |
10 |
3950 |
793.7 |
2650-5300 |
2650 |
2975 |
3500 |
3950 |
4100 |
5200 |
5300 |
| 20 |
10 |
3971.4 |
994.9 |
2750-5900 |
2750 |
2750 |
3400 |
3650 |
4300 |
5900 |
5900 |
| ALS |
| 6 |
10 |
15.8 |
4.3 |
10-21.5 |
10 |
10.5 |
12.5 |
15.3 |
21 |
21.3 |
21.5 |
| 7 |
10 |
14.4 |
3.17 |
10.5-19.5 |
10.5 |
10.5 |
10.5 |
15.5 |
15.5 |
19.5 |
19.5 |
| 8 |
11 |
16.4 |
5.1 |
6.8-23 |
6.8 |
11 |
13 |
17 |
22 |
22 |
23 |
| 9 |
10 |
21.3 |
7.0 |
12.5-31 |
12.5 |
12.5 |
15.5 |
21.5 |
25.5 |
31 |
31 |
| 10 |
10 |
20 |
4.4 |
15.5-30 |
15.5 |
16 |
16.5 |
18.8 |
21 |
27 |
30 |
| 11 |
12 |
21.6 |
7.8 |
9.4-30 |
9.4 |
10 |
14.3 |
24.5 |
28 |
30 |
30 |
| 12 |
13 |
22.9 |
4.3 |
16-29.5 |
16 |
17.5 |
19 |
23 |
25 |
29 |
29.5 |
| 13 |
10 |
21.5 |
6.3 |
8.8-34 |
8.8 |
13.15 |
18.5 |
22.3 |
24 |
29 |
34 |
| 14 |
11 |
24 |
6.4 |
10.5-33 |
10.5 |
19 |
20.5 |
24 |
30 |
32 |
33 |
| 15 |
11 |
29 |
4.9 |
21.5-35 |
21.5 |
23 |
23 |
30 |
34 |
34 |
35 |
| 16 |
10 |
29.4 |
8.2 |
21-46 |
21 |
21.3 |
23 |
27.8 |
37 |
41.5 |
46 |
| 17 |
10 |
31.6 |
10.9 |
18-50 |
18 |
20.5 |
24 |
27 |
39 |
48.5 |
50 |
| 18 |
10 |
30.9 |
8.5 |
16.5-42 |
16.5 |
17.8 |
26.5 |
31.5 |
35.5 |
42 |
42 |
| 19 |
10 |
27.8 |
6.1 |
19-41 |
19 |
21.5 |
25 |
26 |
29 |
37.5 |
41 |
| 20 |
10 |
25.6 |
7.6 |
11.5-37 |
11.5 |
11.5 |
23 |
26 |
28.5 |
37 |
37 |
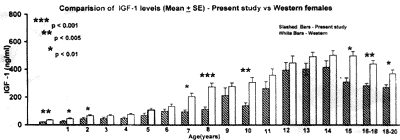
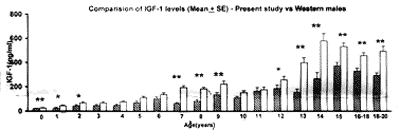
Fig.
1. Comparison of IGF-1 levels (mean ± SE).
We wish to acknowledge
the guidance and support of Dr. Sudha Gangal, Director, Research
Society and Dr. N.C. Joshi, Dean, Bai Jerbai Wadia Hospital for
Children; Deepak, Shamim and Lata helped us in the field work.
Contributors:
MPD helped in designing the study. DB co-ordinated the study
(designing, interpretation of data, drafting of manuscript); she will
act as the guarantor for the paper. RKD helped in sample collection,
performing the tests, data compilation and in drafting the paper. CK
assisted in field work.
Funding:
Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi. ALS kits were
provided as gift by Diagnostic Systems Laboratory, USA.
Competing interests: None
stated.
|
Key
Messages
|
|
Data generated
may be used as reference while evaluating cases of GH disorders.
Difference exist in circulatory levels of IGF-1 in Indian
compared to Western age-matched population.
|
-
Kawai N, Kanzaki
S, Takano-Watou S, Tada C, Yamanaka Y, Miyata T, et al.
Serum free Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1), total IGF-1 and
IGF binding protein-3 concentrations in normal children and
children with growth hormone deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab
1999; 84:82-89.
-
Juul A, Moller S,
Mosfeldt-Laursen E, Rasmussen MH, Scheike T, Pedersen SA, et
al. The acid-labile subunit of human ternary insulin-like
growth factor binding protein complex in serum: Hepatosplanchnic
release, diurnal varia-tion, circulating concerntrations in
healthy subjects and diagnostic use in patients with growth
hormone deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998; 83: 4408-4415.
-
Rosenfeld RG,
Albertsson-Wikland K, Cassorla F, Frasier SD, Hasegawa Y, Hintz
RL, et al. Diagnostic controversy: The diagnosis of
childhood growth hormone deficiency revisited. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab 1995; 80: 1532-1540.
-
Savage MO, Blum
WF, Ranke MB, Postal-Vinay MC, Cotterill AM, Hall K et al.
Clinical features and endocrine status in patients with growth
hormone insensitivity (Laron syndrome). J Clin Endocrinol Metab;
1993; 77: 1465-1471.
-
Frank GR, Cheung
PT, Horn JA, Alfaro MP, Smith EP, Chernausk SD. Predicting the
growth response to growth hormone in patients with intrauterine
growth retardation. Clin Endocrinol 1996; 44: 679-685.
-
Nobel F, Dewailly
D. Puberty and polycystic ovarian sysndrome; The
insulin/insulin-like growth factor hypothesis. Fertility
sterility 1992; 58: 655-666.
-
Juul A, Scheike
T, Nielsen CT, Krabbe S, Muller J, Skakkebaek NE. Serum
insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) and IGF-binding protein 3
levels are increased in central precocious puberty: Effects of
two different treatment regimens with gonadotropin-releasing
hormone agonists, without or in combination with an antiandrogen
(Cyproterone Acetate). J Clin Endocrinol Metab; 1995; 80:
3059-3067.
-
Agarwal DK,
Agarwal KN, Upadhaya SK, Mittal R, Prakash R, Rai S. Physical
and sexual growth patterns of affluent Indian children from 5 to
18 years of age. Indian Pediatr 1992; 29: 1203-1268.
-
Agarwal DK,
Agarwal KN. Physical growth of Indian affluent children (birth-6
years). Indian Pediatr 1994; 31: 377-413.
-
Colaco P, Desai
M. Identification of a child with short stature. Indian Pediatr
1990; 27: 1159-1164.
-
Khadgawat R,
Dabadghao P, Mehrotra RN, Bhatia V. Growth charts suitable for
evaluation of Indian Children. Indian Pediatr 1998; 35: 859-865.
-
Diagnostic System
Laboratories, Inc. Kit inserts for IGF-1 (Catalogue no: DSL
2800), IGFBP-3 (Catalogue no : DSL 6600) and ALS (Catalogue no:
DSL-10-8200).
-
Juul A, Bang P,
Hertel NT, Main K, Dalgaard P, Jorgensen K, et al. Serum
insulin-like growth factor-1 in 1030 healthy children,
adolescents and adults; Relation to age, sex, stage of puberty,
testicular size and body mass index. J Clin Endocrinol Metab
1994; 78: 744-752.
-
Argente J,
Barrios V, Pozo J, Munoz MT, Hervas F, Stene M, et al.
Normative data for insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), IGF-binding
proteins, and growth hormone- binding protein in a healthy
Spanish pediatric population: Age- and sex-related changes. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab 1993; 77: 1522-1528.
-
Vijayaraghavan K,
Singh D, Swaminathan MC. Heights and weights of well-nourished
Indian school children. Indian J Med Res 1971; 59: 648-654.
|
