|
|
|
Indian Pediatr 2019;56: 981 |
 |
Inverse
Pityriasis Rosea
|
|
Nadia Ghariani Fetoui* and Lobna Boussofara
Dermatology Department, Farhat Hached University
Hospital , Ibn Jazzar Avenue, Sousse, Tunisia
*[email protected]
|
|
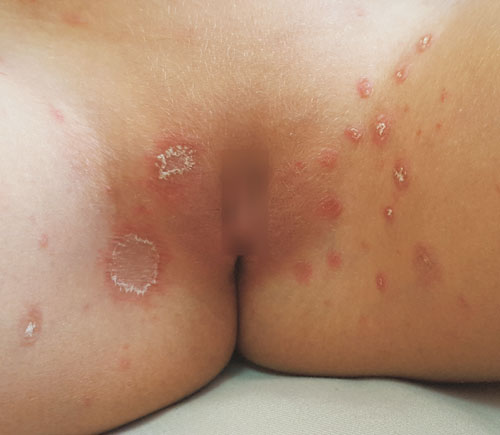
An 11-year-old previously healthy girl presented
with an acute eruption in inguinal folds. Examination revealed a 3 cm
erythematous and annular patch with peripheral collarette scaling and
fine wrinkling in the center, associated with similar but smaller
lesions, limited to the groins (Fig. 1). The rest of the
physical examination, including mucous membranes and skin folds was
within normal limits. Mycologic evaluation ruled out dermatophytosis.
The diagnosis of pityriasis rosea was made based on the presence of a
herald patch and the acute onset of lesions, despite their atypical
topography.
 |
|
Fig.1 Inverse pityriasis rosea
limited to the groins, in an 11-year-old girl.
|
Pityriasis rosea usually occurs in young healthy
persons between the ages of 10 and 35, and is commonly located on the
trunk. In children and adolescents, lesions may be concentrated in the
inguinal and axillary areas, defining the inverse variety. The main
differential diagnoses include fungal infections associated with
intertrigo (KOH-positive annular scaling patches, growing
centrifugally), atopic dermatitis (chronic relapsing and highly pruritic
dermatitis with predominant flexural involvement in old children),
nummular eczema (coin-shaped papulo-vesicular erythematous lesions),
inverse psoriasis (erythematous, shiny, moist plaques in intertriginous
areas, with no scale), infantile seborrheic dermatitis (ill-defined
erythematous patches associated with fine pityriasiform scaling) and
drug eruption (benign and self-healing eruption occuring with high-dose
chemotherapy protocols). The eruption spontaneously fades within 6
weeks.
|
|
|
 |
|

