A 2-year-old boy presented to us with multiple nodular lesions without
any itching or pain all over the body (Fig. 1 and
Fig. 2) for last 2 months. Child was healthy, alert, a
febrile, and had no visual defect. Skin biopsy showed proliferation of histiocytes with
presence of touton giant cells, and positive for CD68. We diagnosed him
as having Juvenile xanthogranuloma and kept him on follow-up.
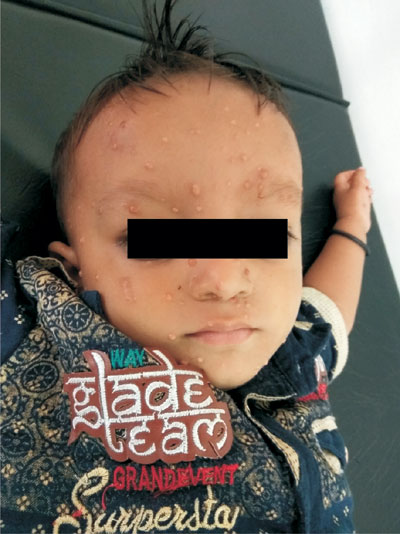 |
|
Fig. 1 Multiple small nodules present all over face
except mucous membrane.
|
|

|
|
Fig. 2 Nodular lesions present over perianal, scrotal
and thigh.
|
Juvenile xanthogranuloma (JXG) is a disorder related
to a group of non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis. This disease typically
affects infants and small children. Red and brown papules or nodules
(often with a golden yellow tinge) are located in any part of the body;
mucosal lesions are rare. In rare cases, it can involve eye-resulting in
blindness as a consequence of glaucoma and bleeding in to the anterior
chamber. Multinucleated giant cells (Touton cells) are observed on
histopathology. They have a ring of nuclei around high lipid content
cytoplasm. Immunohistochemical staining plays a key role in diagnosis;
CD68 and vimentin are positive, whereas CD1a is usually negative.
Differential diagnoses are Langerhans cell
histiocytosis, pyogenic granuloma, Spitz nevus, urticaria pigmentosa,
xanthomas and molluscum contagiosum. Juvenile xanthogranuloma may be
associated with neurofibromatosis type I and myelomonocytic leukemia.
Spontaneous regression usually occurs within 1-3 years and recurrence is
rare. Large size nodules or cosmetic reasons are the main indication for
surgical removal of nodules. Chemoradiotherapy, immunosuppression
(steroids, cyclosporine, methotrexate) and surgery have be used in
systemic cases.

