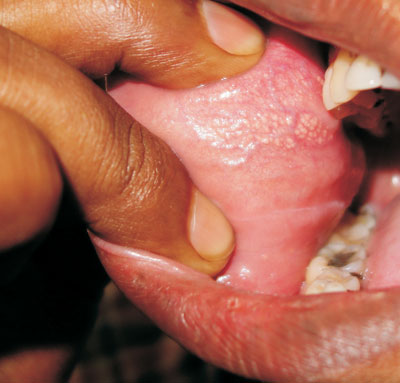
A 14-year-old boy presented with gradually increasing, asymptomatic
white elevations over the mucosa of right cheek since 4 years of age.
There was no history of tobacco abuse, and the past medical history and
family history were unremarkable. Examination showed clusters of small
white papules with smooth shiny surface on the right cheek (Fig.
1). The lesions could not be scraped off. Rest of the mucocutaneous
and systemic examination was normal. The condition was diagnosed as
Fordyce spots and the parents were reassured.
 |
|
Fig. 1 Fordyce spots on mucosa of right
cheek.
|
Fordyce spots are ectopically located
visible sebaceous glands on the genitals, lips and oral cavity,
vermillion border of the lips being the commonest site. They appear as
small, painless, raised, pale, red or yellow-white spots of 1 to 3 mm
diameter. Their presence is considered as normal anatomic variants
rather than a true medical condition. They are not usually visible in
young children, and tend to appear at about 3 years of age increase
during puberty and become more obvious in later adulthood. The condition
needs to be differentiated from candidiasis (easily detachable white
pseudomembranes), leukoplakia (adherent white plaque often with fissured
surface) and white sponge nevus (thick, velvety, white spongy-looking
plaques on buccal mucosa). No treatment is required; CO

