|
|
|
Indian Pediatr 2019;56:
506 |
 |
Catastrophic Cough in a
Young Infant
|
|
B Banupriya1
and A Jagadeesh2
Department of Paediatrics, Mahatma Gandhi Medical
College and Research Institute, Sri Balaji Vidyapeeth University,
Puducherry, India.
Email: [email protected]
|
|
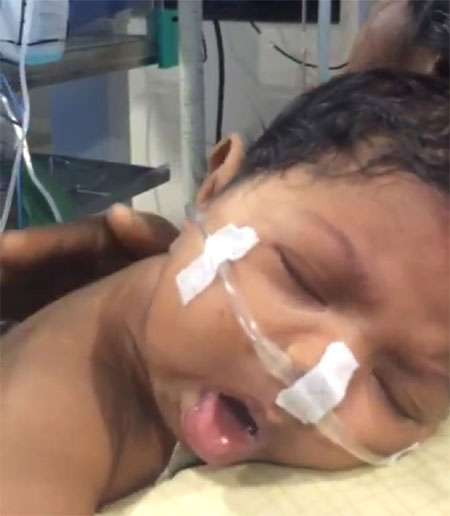
A 45-day-old girl child presented with cough for 10
days, with increasing frequency and duration of cough bouts over the
past two days. There was no fever or respiratory distress. Child had
characteristic ‘whooping cough’– prolonged cough bouts ending in
inspiratory whoop (Web Video 1 and Fig. 1).
Complete blood count showed total leukocyte count of 26800 cells/mm
3
with 75% lymphocytes. Chest X-ray was
normal. Child was treated with oral azithromycin for 5 days, suspecting
pertussis. On day 2 of hospitalization, child had prolonged cough bouts
associated with hypoxia and apneic spells requiring intubation.
Nasopharyngeal swab for Bordetella pertussis PCR was reported to
be positive. Child was extubated after 4 days of mechanical ventilation
as the frequency of cough bouts on ventilator reduced. Child needed
oxygen support during cough bouts even after extubation, and was
gradually weaned off oxygen over 14 days. At discharge, child had cough
bouts with reduced severity and no hypoxia. Further questioning revealed
that child was scheduled for her first dose of DTP vaccine next week and
mother had received TT vaccine, not Tdap, during her antenatal visits.
On follow-up, child was thriving well, had occasional cough episodes,
and had been immunized with 3 doses of DTP vaccine.
 |
|
Fig. 1 Infant with whooping cough
(see video at website).
|
Cough in children may sound benign, but sometimes it
may be harbinger of serious underlying diseases like pneumonia,
bronchiolitis or Pertussis. Differential diagnosis of child with
prolonged acute cough include Postviral cough, Pertussis, Persistent
bacterial bronchitis, Bronchiolitis, Pneumonia or Retained foreign body.
Pointers useful in differentiating pertussis from these conditions
include characteristic inspiratory whooping sound of cough, cough bouts
escalating at 7-10 days, apneic spells or cyanosis in infants, and
presence of leukocytosis with >50% lymphocytes.
|
|
|
 |
|

