|
|
|
Indian Pediatr 2014;51: 501 |
 |
Prenatal Detection of Fanconi Anemia
|
|
Avani Solanki and Babu Rao Vundinti
National Institute of Immunohematology (ICMR), KEM
Hospital Campus, Parel, Mumbai, India.
Email: [email protected]
|
|
Fanconi anemia (FA), a clinically heterogeneous disorder with incidence
of 1 in 350,000 births, is characterized by bone marrow failure (aplastic
anemia), developmental delay, physical abnormalities, and increased risk
of solid tumors and leukemia [1,2]. Chromosomal breakage investigation
using DNA interstrand cross-linking agents such as diepoxybutane (DEB),
and Mitomycin C (MMC) is the gold standard for the diagnosis. Molecular
studies have so far identified 15 genes that can have mutations in FA
patients [3,4]. We describe prenatal diagnosis of FA by cytogenetic and
molecular analysis.
A 5-year-old girl having hypoplastic anemia was
referred to us for chromosomal breakage studies. Chromosomal analysis
from peripheral blood cultures induced with mitomycin C (MMC) (40 ng/mL)
revealed a high frequency chromosomal breakage (8.6 breaks/cell)
compared to controls (0.062 breaks/cell) (Fig.1). Western
blot for FANCD2 confirmed the upstream gene defects in FA
pathway. Molecular analysis of proband showed heterotzygous c.1303C>T
(rs148473140: R/C) mutation in FANCA gene. Father was found to be
carrier for the mutation and the mother was normal. In the next
pregnancy, chorion villus sample was aspirated at 12 weeks of gestation
and mutational analysis of FANCA gene showed c.1303C>T mutation
in genomic DNA of the fetus.
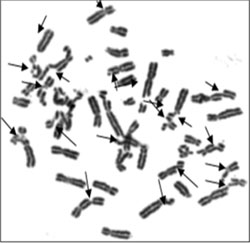 |
|
Fig. 1 Metaphase
showing chromosomal breakage and radial
formation.
|
The chromosomal breakage study for the diagnosis of
FA is available in few cytogenetic laboratories. However, the diagnosis
of FA by chromosomal breakage study from chorionic villi or amniotic
cell culture is time consuming and there are chances of getting false
positives and negatives. Molecular level study by mutation analysis, on
the other hand, is a rapid and accurate method for diagnosis of proband
and subsequent pregnancies.
References
1. Gillio AP, Verlander PC, Batish SD, Giampietro PF,
Auerbach AD. Phenotypic consequences of mutations in the Fanconi anemia
FAC gene: an international Fanconi anemia registry study. Blood.
1997;90:105-10.
2. GraciaHiguera I, Taniguchi T, Ganesan S, Meyn MS,
Timmers C, Hejna J, et al. Interaction of the Fanconi anemia
proteins and BRCA1 in a common pathway. Mol Cell. 2001;7:249-62.
3. deWinter JP, Joenje H. The genetic and molecular
basis of Fanconi anemia. Mutation Research. 2009;668:11-9.
4. Vaz F, Hanenberg H, Schuster B, Barker K, Wiek C,
Erven V, et al. Mutation of the RAD51C gene in a Fanconi anemia-like
disorder. Nature Gene. 2010;42:406-9.
|
|
|
 |
|

