|
|
|
Indian Pediatr 2011;48: 583-584 |
 |
Multiple Discharging Sinuses with Disseminated
Dactylitis |
|
Vishal Kumar and Manish Kumar
Department of Pediatrics, Maulana Azad Medical College &
Associated Chacha Nehru Bal Chikitsalya,
Geeta Colony, Delhi, India.
Email: [email protected]
|
|
A 10-year-old male presented with fever, cough, poor oral acceptance,
weight loss, and multiple painless swellings associated with
serosanguineous discharge for last six weeks. He had already received
multiple courses of antibiotics before presenting to us. On examination,
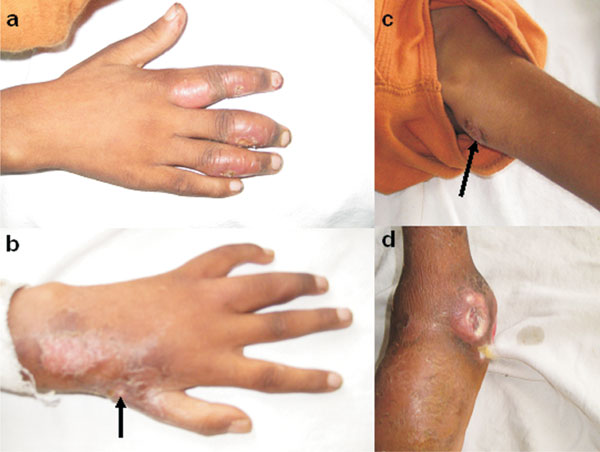
four spindle shaped swellings with discharging sinuses were present over
right index, middle and ring fingers. There were two discharging sinuses
present over the dorsum of left hand and on the medial aspect of left
thigh. An ulcer with discharging sinus was present over lateral aspect of
left ankle (Fig. 1). He was severely wasted. Hands X-ray
revealed multiple lytic lesions with little periosteal reaction in
underlying respective phalanges and metacarpal bones. Chest X-ray showed
nodular miliary shadows. The Ziehl-Neelsen staining of the
discharges taken separately from all discharging sinuses, demonstrated
acid fast bacilli. After one month of antitubercular treatment, all
discharging sinuses completely healed.
 |
|
Fig.1 (a)Spindle shaped swellings with discharging sinuses
over index, middle and ring fingers of right hand, (b) Discharging
sinus present over the dorsum of left hand, (c) Discharging sinus
present over left thigh, (d) An ulcer with discharging sinus over
left ankle.
|
Tuberculosis (TB) of metatarsals, metacarpals and
phalanges is usually associated with active pulmonary involvement, as
observed in present case. TB of phalanges results in characteristic
spindle shaped swelling of fingers, a condition known as spina ventosa.
Spina is a latin word for "short bone" and ventosa is a latin word for
"inflated with air". The differential diagnosis of such a swelling
includes syphilis and sickle cell dactylitis. Disseminated tubercular
dactylitis, as seen in this case has been reported very rarely.
Differentials for multiple discharging sinuses in children include
staphylococcal infection and mucormycosis, both are rapidly progressive in
nature, and later is associated with necrosis of skin and subcutaneous
tissue leading to eschar formation. Other gradually progressive diseases
presenting as discharging sin-uses in children are actinomycosis,
botryomycosis, nocardiosis, and sporotrichosis. Sinus tracts of
actinomycosis and nocardiosis usually discharge granules; botryomycosis is
associated with subcutaneous nodules and large verrucous (wart-like)
lesions; and in sporotrichosis an ascending chain of nodules develops
along skin lymphatic channels (nodular angiitis).
|
|
|
 |
|

