A 21-month-old girl with global developmental delay and failure to
thrive presented with painful swelling of the right leg for 4 days.
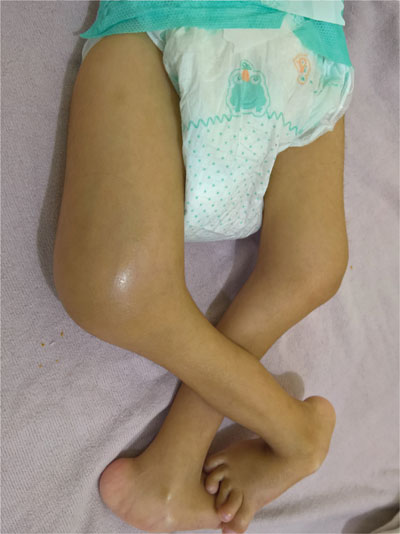
Examination revealed tender swelling (Fig. 1a) and
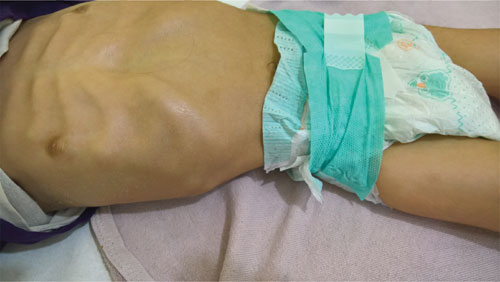
restricted movements of right leg. Costochondral rosary and hemorrhagic
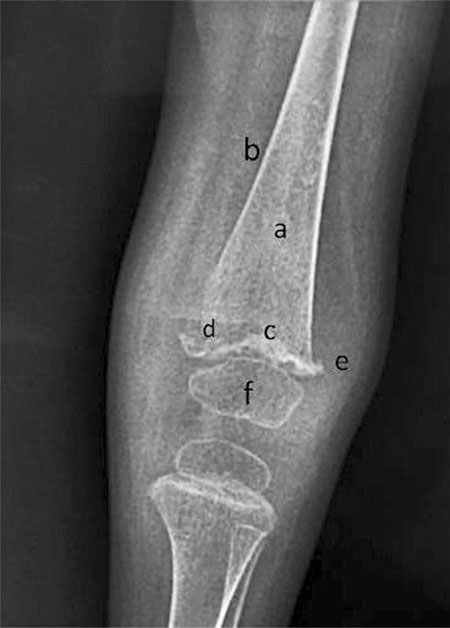
gums were also noted Lower extremity radiographs (Fig. 2)
showed findings typical of scurvy. Treatment with oral vitamin C led to
rapid improvement.
 |
|
(a)
|
(b) |
|
Fig. 1 Diffuse (tender) swelling of
right leg above knee (a); and . Costochondral beading of ribs
(b).
|
 |
|
Fig. 2 Lower extremities radiograph
showing (a) ground glass appearance of the bones; (b)
pencil-thin cortices; (c) white dense line of metaphyseal
calcification - Fraenkelís line; (d) an adjacent radiolucent
band - Trummerfeld zone; (e) lateral metaphyseal beaking -
Pelkan spur; and (f) central rarefaction with peripheral
calcification of epiphyses - Wimberger sign.
|
Infantile scurvy results from lack of intake of
vitamin C rich foods such as fresh fruits and vegetables. Affected
infants present with irritability, failure to thrive, swollen and
painful extremities with restriction of movements (pseudoparalysis),
frog posture, gum bleeding, and scorbutic rosary. Characteristic
radiological findings and rapid response to treatment with vitamin C
confirms the diagnosis. Differential diagnoses include traumatic injury,
septic arthritis/osteomyelitis, hemophilic hemarthrosis, congenital
syphilis, leukemic infiltration and other painful conditions.
Costochondral beading may suggest the diagnosis of rickets but rachitic
rosary is round and non-tender, while rosary in scurvy is sharp and
tender. All these conditions can generally be distinguished by the
presence of associated clinical features such as fever, rash, or trauma.
Ancillary investigations and radiography help in confirming the
diagnosis.

