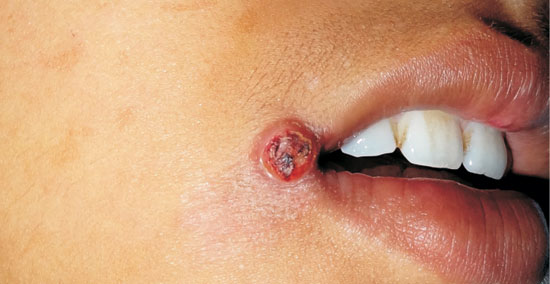
A 7-year-old girl presented with solitary, asymptomatic,
nodule near right angle of mouth for 8 months. The lesion
started as a small papule and increased in size over time.
The child was otherwise healthy. On examination, single
erythematous nodule measuring 1 cm, and of soft to firm
consistency, was seen near the right angle of mouth. The top
of the lesion was eroded and covered with crust. Rest of the
muco-cutaneous examination was unremarkable (Fig.
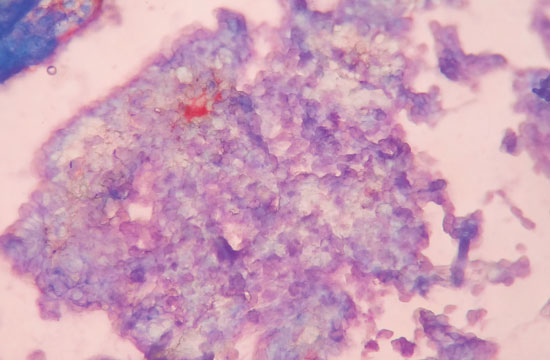
1). During examination, whitish paste like material was
expressed during palpation. Giemsa stain of the material
showed faint bluish cytoplasmic inclusions (Fig. 2).
The lesion was removed by shave excision and was sent for
histopathology. The histopathology findings were acanthosis
and eosionphilic cytoplasmic inclusions, confirming the
diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum. Family members were
examined and classical molluscum contagiosum lesions were
noted in brother (left temple region) and mother (abdomen).
After shave excision, oral and topical antibiotic was
advised for 7 days; the lesion resolved completely in 2
weeks, without any sequale.
 |
|
Fig. 1 Erythematous crusted
nodule at the angle of mouth.
|
 |
|
Fig. 2 Pale blue
cytoplasmic inclusions (Giemsa stain X 400).
|
Solitary molluscum contagiosum poses a
diagnostic challenge and is confused with keratoacanthoma
(firm lesion with central keratin material) and granuloma
pyogenicum (soft friable lesion with history of bleeding on
minor trauma or spontaneously). Cytopathology can be helpful
in rapid diagnosis of such lesions.

