A 3-day-old full term male neonate was admitted with history of bilious
vomiting since birth. On examination, he had a prominent white forelock
of hair and massively distended abdomen. Audiologic evaluation (BERA)
revealed complete bilateral sensorineural hearing loss. A clinical
diagnosis of Shah-Waardenburg syndrome or Waardenburg syndrome type 4
was made. The abdominal roentgenogram revealed dilated bowel loops but
no air-fluid levels. Barium enema showed a featureless normal caliber
colon with no obvious transitional zone; the small bowel loops were
distended.
On failure of conservative management, an exploratory
laparotomy was undertaken on D18 of life that revealed distended
proximal jejunal and ileal loops; the 15 cm of terminal ileum and the
colon were contracted (Fig.1). Multiple sero-muscular biopsies
were taken from colon and terminal ileum; appendectomy was also
performed. A divided ileostomy was performed at the transition zone. The
histopathology of gut biopsies confirmed aganglionosis in colon and
terminal ileum. Child underwent modified Kimura’s procedure at 10 weeks
of age but later succumbed to sepsis at 3 months of age.
 |
|
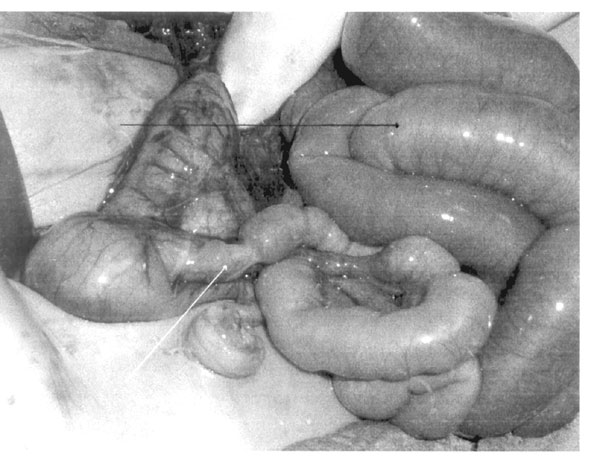
Fig. 1. Intra-operatively, the colon and distal
ileum were found contracted (white arrow); the ileum proximal to
the transition zone was distended (black arrow).
|
Waardenburg syndrome (WS) was first described in 1951
(now called WS type 1) with 6 components lateral displacement of the
medical canthi combined with dystopia of the lacrimal puncta and
blepharophimosis, prominent broad nasal root, hypertrichosis of the
medial part of the eyebrows, white fore-lock, heterochromia iridis and
deafmutism(1). WS4 is the association of Waardenburg syndrome with
Hirschsprung disease. Only 48 cases are reported in English literature
till 2002(2).
Y.K. Sarin,
V. Manchanda,
Department of Pediatric Surgery,
Maulana Azad Medical College,
New Delhi 110 002, India.
E-mail: [email protected]
1. Waardenburg PJ. A new syndrome combining
developmental anomalies of the eyelids, eyebrows and nose root with
pigmentary defects of the iris and head hair and with congenital
deafness. Am J Hum Genet 1951; 3: 195-253.
2. Toki F, Suzuki N, Inoue K, Suzuki M, Hirakata K, Nagai K, et
al. Intestinal aganglionosis associated with the Waardenburg
syndrome: report of two cases and review of the literature. Pediatr
Surg Int. 2003; 19: 725-728.
