|
Single cell abnormality is defined as the chromosome
abnormality which occurs in one metaphase plate, the same is not seen when more
metaphases are scored(1). Single cell translocations have been previously
reported to occur in normal lymphocyte cultures. A number of investigators have
reported the frequent occurrence of translocation involving chromosome 7 and
14(1,2). We have observed this single cell abnormality involving chromosomes 7
and 14 in PHA stimulated blood from a 1-year-old male child. The child had a
history of mental retardation and seizure disorder. The single cell
translocation was first detected in 25 cells and when 75 additional cells were
analyzed no further occurrence of translocation was observed. The break points
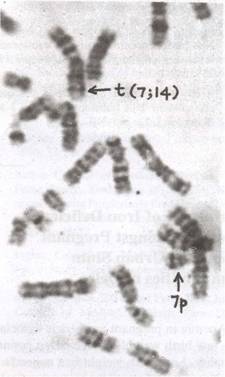
were identified to be on 7p 12 and 14q 12 regions (Fig. 1). The
pathogenesis of these abnormalities has not yet been clearly understood(3,4). In
our routine cytogenetic screening, single cell abnormality was found as random
chromosome loss or gain in cases such as bad obstetric history and spontaneous
repeated abortions. To rule out the occurrence of single cell translocations, we
have set up two, different blood lymphocyte cultures, namely, blood ,culture
induced with high dose of PHA, and long hypotmic treatment. In the latter random
chromosome loss or gain was observed. Our in vitro study results suggest
that the random chomosome loss gain sometimes may be accidental or due to a
technical artefact, but the structural abnormalities occurring in single cells
may have a definite
role in the disease development as mosaic, where a greater number cells
may need,to be analyzed or cells from fibroblasts may need to be cultured to
identify mosaicism. Single cell abnormalities might indicate the presence of
parental mosaicism. Hence there is an urgent need to rule out parental mosaicism
in such a case to enable appropriate genetic counseling to the family.
 |
|
Fig. 1. Partial
metaphase showing translocation between 7 and 14
chromosome, i.e., t (7;14) (p12;q11)
and deleted part of7p. |
V. Babu Rao,
Bibhas Kar,
Insiitute afGenetic Studies,
Rajkamal Complex,
Panchsheel Square,
Nagpur-10,
India
1. Beatty - De Sana J, Hoggard M, Cooledge J. Non-random occurrence of
7-14 translocations in human lymphocyte cultures. Nature 1975; 255:
242-243.
2. Reddy K, Thomas I. Significance of acquired non-random 7/14
translocations. Am J Med Genet 1985; 22: 305-310.
3. Higgins MD, Palmer CG. Single cell translocatios in couples with
multiple spontaneous abortions. Hum Genet 1987; 75: 24-27.
4. Murre C, Waldmann R, Morton .c, Bongiovanni K, Waldmann T, Shows T,
et al. Human gammachain genes are rearranged in leukaemic T cells
and map to the short arm of chromosome 7. Nature 1985; 316: 549-552.
|
