A male child born with rhesus-isoimmunisation was treated
with double volume exchange transfusion followed by
phototherapy for 96 hours. On day 10, he was found to have
conjugated hyperbilirubinemia which gradually progressed
(maximum value, 42 mg/dL; conjugated fraction, 32 mg/dL on
day 30). Hepatobiliary-iminodiacetic-acid (HIDA) scan showed
delayed clearance. He received phenobarbitone for five days,
keeping the possibility of inspissated bile plug syndrome.
Gradually the bilirubin level decreased to 6mg/dl by 2
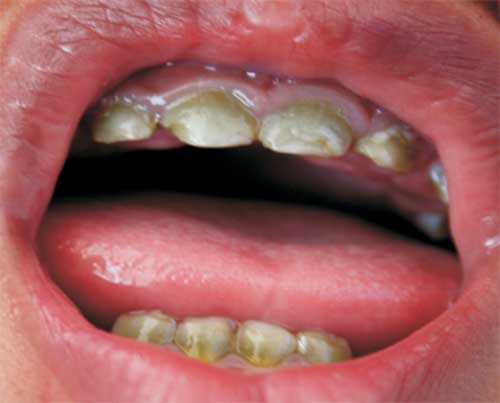
months of age. The baby had eruption of deciduous teeth at 7
months of age which were green-to-black stained. At current
age of 18 months, all the teeth are green-to-black stained (Fig.
1).
 |
|
Fig.1 Green-to-black
stained deciduous teeth.
|
Hyperbilirubinemia causes reversible
staining of all tissues except the teeth. In the latter,
bilirubin is permanently trapped because of loss of
metabolic activity after maturation. Differential diagnosis
of green teeth includes – neonatal cholestasis (e.g.,
biliary atresia, sepsis, pathological hyperbilirubinemias,
and metabolic diseases), hemolytic-anemia, congenital
hyporthyro-idism, hepato-biliary problems, and drug
administration. Treatment options include; composite resin
restorations, bleaching techniques, and use of
transillumination with ultraviolet light.

